- UNSW
- ...
- UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology
- Our research
- Membrane material development
- Development of high performance nanocomposite filtration membranes
- Home
- About us
-
Our research
- Membrane material development
-
Water treatment
- Study of floc strength and stability during direct filtration of surface water
- Mass and heat transfer in submerged vacuum membrane distillation and crystallization
- Development of novel membrane integrity tests for virus sized particles
- Reuse of old reverse osmosis membranes used in desalination plants | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
- Optimisation of hybrid coagulation/submerged membrane bioreactor treatment of wastewaters | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
- Developing national validation guidelines for MBRs in water recycling
- Assisted forward osmosis for energy savings in RO desalination
- Characterising nanostructure functionality of conventional and advanced polymeric membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy
- Optimising low-pressure membrane pre-treatment for desalination | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
-
Process design & modelling
- Computational fluid dynamics modelling of Membrane Bioreactors
- Resilience modelling of advanced water treatment plants
- Mechanical reliability of microporous membranes in water recycling applications
- Optimisation of Membrane Distillation Processes
- Feedback Destabilizing Control of Electro-osmotic Flow
- Greenhouse gas technology
- Bio-separations
-
Food & agriculture
- Membrane facilitated subsurface drip irrigation
- Milk ultrafiltration
- Protein recovery from potato processing water using ultrafiltration membrane
- Phosphorus recovery from wastewater
- Sequential chemical and enzymatic cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes in dairy applications
- Application of membrane separation process in concentration and separation of polyphenol compounds for evaluation of their health benefits
- Optimising low-pressure membrane pre-treatment for desalination
-
Archived research projects
- Composite biocatalytic nanoflower
- Superhydrophobic Membranes for Membrane Distillation Applications
- Polymers for Isoporous and Functional Membranes
- Separation performance of dip-coated microporous hollow fibre polymer inclusion membranes (PIM)
- Improvement in Fouling Release Properties of Ultrafiltation PVDF Membranes
- Thin Film Nano-composite Membrane Fabrication for Carbon Dioxide Capture from Flue Gas
- MOF based highly efficient gas separation membrane
- Biocatalytic membrane reactors for greenhouse gas capture
- Evaluation of CO2 Capture with High Performance Hollow Fiber Membranes from Flue Gas: A Pilot Scale Study
- Improved Carbon Dioxide Separation Performance with Additives of PEO/PDMS Copolymer in PPO Membranes
- Our facilities
- Our services
- Contact us
- Home
- About us
-
Our research
Water treatment
- Study of floc strength and stability during direct filtration of surface water
- Mass and heat transfer in submerged vacuum membrane distillation and crystallization
- Development of novel membrane integrity tests for virus sized particles
- Reuse of old reverse osmosis membranes used in desalination plants | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
- Optimisation of hybrid coagulation/submerged membrane bioreactor treatment of wastewaters | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
- Developing national validation guidelines for MBRs in water recycling
- Assisted forward osmosis for energy savings in RO desalination
- Characterising nanostructure functionality of conventional and advanced polymeric membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy
- Optimising low-pressure membrane pre-treatment for desalination | UNESCO Centre for Membrane Science and Technology - UNSW Sydney
Process design & modelling
- Computational fluid dynamics modelling of Membrane Bioreactors
- Resilience modelling of advanced water treatment plants
- Mechanical reliability of microporous membranes in water recycling applications
- Optimisation of Membrane Distillation Processes
- Feedback Destabilizing Control of Electro-osmotic Flow
Food & agriculture
- Membrane facilitated subsurface drip irrigation
- Milk ultrafiltration
- Protein recovery from potato processing water using ultrafiltration membrane
- Phosphorus recovery from wastewater
- Sequential chemical and enzymatic cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes in dairy applications
- Application of membrane separation process in concentration and separation of polyphenol compounds for evaluation of their health benefits
- Optimising low-pressure membrane pre-treatment for desalination
Archived research projects
- Composite biocatalytic nanoflower
- Superhydrophobic Membranes for Membrane Distillation Applications
- Polymers for Isoporous and Functional Membranes
- Separation performance of dip-coated microporous hollow fibre polymer inclusion membranes (PIM)
- Improvement in Fouling Release Properties of Ultrafiltation PVDF Membranes
- Thin Film Nano-composite Membrane Fabrication for Carbon Dioxide Capture from Flue Gas
- MOF based highly efficient gas separation membrane
- Biocatalytic membrane reactors for greenhouse gas capture
- Evaluation of CO2 Capture with High Performance Hollow Fiber Membranes from Flue Gas: A Pilot Scale Study
- Improved Carbon Dioxide Separation Performance with Additives of PEO/PDMS Copolymer in PPO Membranes
- Our facilities
- Our services
- Contact us
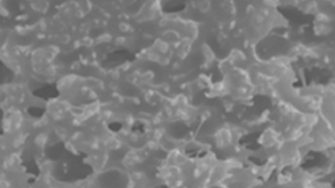
The occurrence of potentially harmful micro-pollutant compounds such as pharmaceutically active chemicals (PhACs), hormones, pesticides and endocrine disrupters (EDC) in the water environment has attracted increasing research interest in the last few years. Traditional membrane water processes cannot effectively remove those chemicals due to the potential adsorption in membranes and accumulation in the water treatment cycle. Laccase has been shown as an effective enzyme to remove micro-poll...
The occurrence of potentially harmful micro-pollutant compounds such as pharmaceutically active chemicals (PhACs), hormones, pesticides and endocrine disrupters (EDC) in the water environment has attracted increasing research interest in the last few years. Traditional membrane water processes cannot effectively remove those chemicals due to the potential adsorption in membranes and accumulation in the water treatment cycle. Laccase has been shown as an effective enzyme to remove micro-pollutants and its stability can be improved by immobilization. In this work, both bio-catalytic nanoparticles and bio-catalytic membranes have been prepared for investigation. Laccase was immobilized on both TiO2 nanoparticles and in-house manufactured flat sheet membranes.
Results have shown modified TiO2 can better retain the enzyme activity than the unmodified TiO2 particles. To form bio-catalytic membranes, laccase has been successfully immobilized on TiO2 functionalized membrane using passive adsorption method. The effect of TiO2 modification and membrane post treatment on enzyme adsorption loading and activity were also investigated. Higher enzyme activity with better stability was found for enzyme immobilized on TiO2 nano- structured membrane than on the controlled PES membrane.
We are currently extending this work by conducting kinetics analyses for the immobilized enzyme.
